Charlie Bilello analyzed the relationship between market valuation and future returns (over various time horizons) in a recent post Valuation, Timing, and a Range of Outcomes. The post contained some very insightful tables, such as the one below, where he shows that valuations matter... if you pay less for stocks, you will generally be provided with higher returns (on average) over almost all time frames.
The Case for Momentum
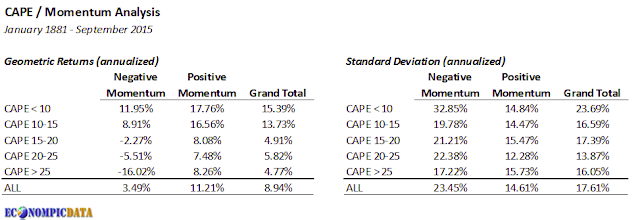
In a previous post Valuations Do Matter (Even Over Shorter Time Frames) / Momentum Driven Valuation Timing, I highlighted a similar point and in addition took a look at how stocks performed at various valuation levels when 12-month returns had been positive or negative. The takeaway (highlighted in the table below) was that market returns were generally strong when stocks were:
- Cheap (with positive or negative momentum)
- Expensive with positive momentum
To bring this full circle, the tables below replicate Charlie's analysis, but also compares those results with the average forward return for a momentum strategy with the following rules (note the returns in the table below differ slightly from Charlie's - not sure what data he used, but I used data from Ibbotson's):
- If the CAPE of the S&P 500 was within the bottom 50th percentile (which happens to be less than 17x), allocate to stocks; otherwise...
- If the S&P composite had a one year backward looking return that was positive, allocate to stocks
- If the S&P composite had a one year backward looking return that was negative, allocate to cash (t-bills)
The case for trend following when markets are expensive becomes abundantly clear when viewed in chart form... when markets are cheap, an allocation to stocks resulted in returns that were on average exactly the same as a buy-and-hold strategy over the short-term and returns that were broadly in-line with those of a buy-and-hold over longer periods. When markets were stretched, momentum protected an investor from severe drawdowns over shorter periods and allowed returns to on average compound over longer periods.